Chainlink is a decentralized network of nodes that exchange data between off-blockchain and on-blockchain smart contract sources via oracles. Many crypto investors consider Chainlink (LINK) to have become a blue-chip DeFi token to invest in. In this blog, we explain how LINK works and what its success and potential are based on.
Chainlink Explained
Chainlink was launched in June 2017 by a company called SmartContract Ltd. The first implementation of Chainlink came out during the same month. Chainlink’s whitepaper was published in September 2017. After the whitepaper, an ICO funding round quickly followed and gathered $32 million. The said amount represents 35 percent of the total LINK supply (1 billion LINK units).
Chainlink’s LINK token is based on the Ethereum blockchain — the ERC-20 and ERC-677 protocols.
The Brief History of Chainlink
2014: Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis launch SmartContract Ltd. (the parent company).
2014-2017: development phase.
2017 September: whitepaper published.
2017 September: ICO funding round raised $32 million.
2019: Chainlink for Ethereum mainnet launched.

What is Chainlink: LINK in Numbers
To begin with, the Chainlink’s native token LINK price performance has been exceptional by all metrics, generating huge retail interest over the years. LINK has ascended +9372,88 percent since its inception. Meanwhile Bitcoin (BTC) has grown +1300,77%, and Ethereum (ETH) +612,70% within the same timeframe.
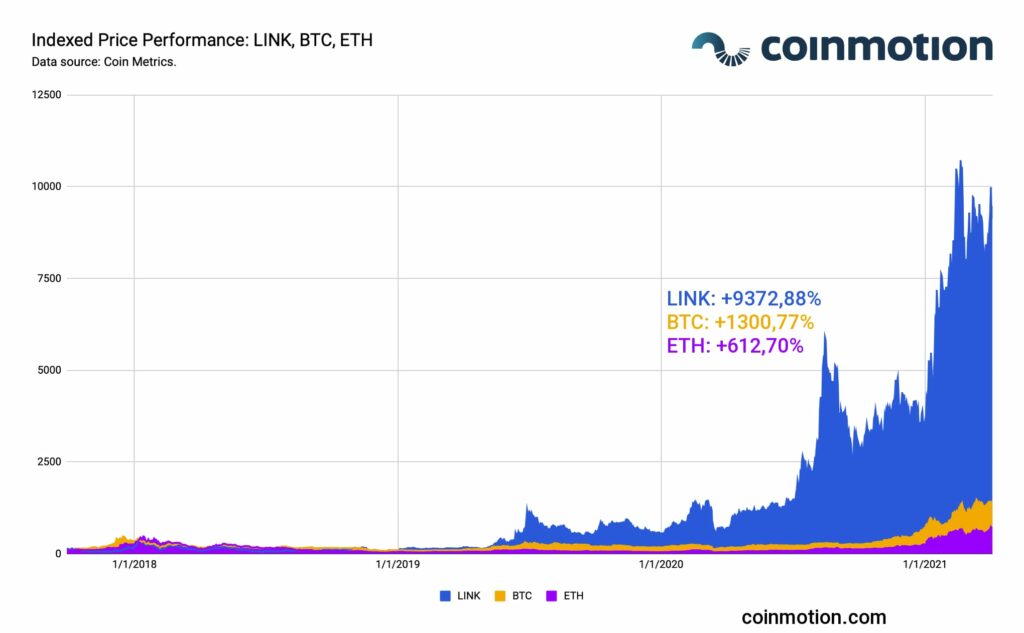
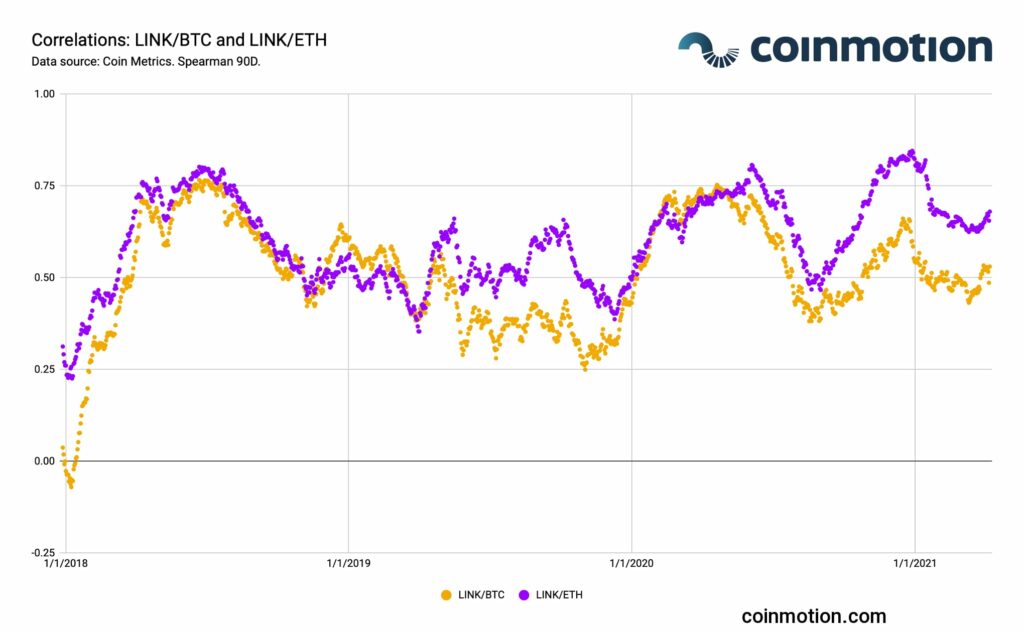
The LINK token price has systematically correlated with Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). There has been an average LINK/BTC correlation of 0,51 and LINK/ETH correlation of 0,59, respectively. LINK’s price performance has outperformed both leading assets. Therefore, the correlation has by default weakened during LINK’s huge price spurts.
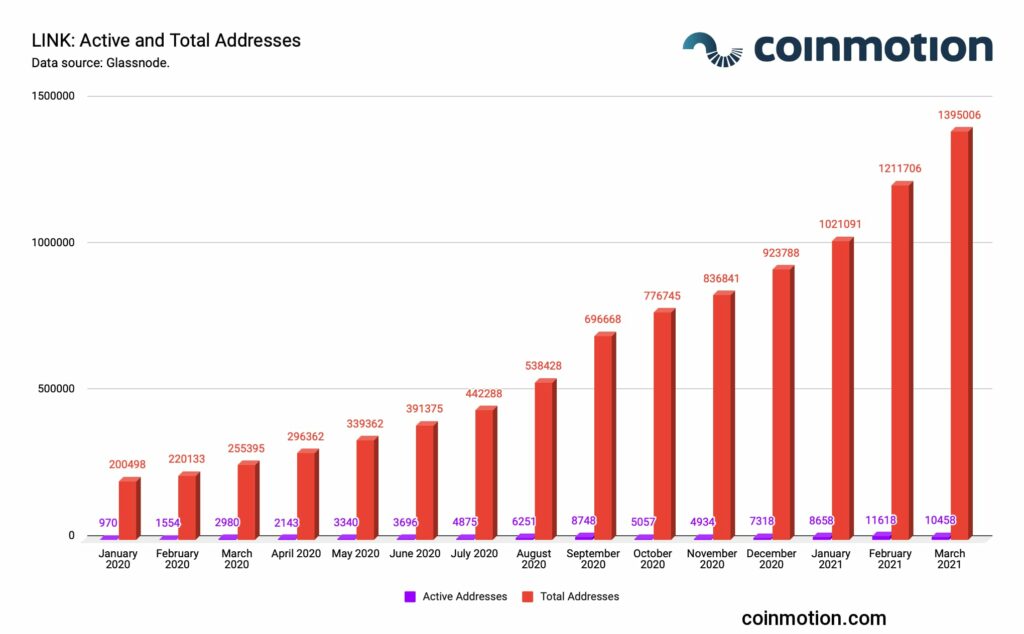
In addition to LINK’s growing price performance, network fundamentals also indicate long-term support for network growth. Since early 2020, Chainlink’s number of addresses has increased by almost 600% and amount of active addresses — by 978%.
Chainlink’s Value Proposition
”Definite truth for me is what blockchains generate in general. They generate a final immutable record that can’t be changed or modified. And the fact that they generate this uniquely immutable record makes the record essentially true. That truth is confirmed by multiple independent sources.” – Sergey Nazarov.
Challenge: Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, initially conceived in 1993, form the core of most blockchain applications. Compared to standard contracts that are enforced by law, smart contracts are backed by cryptographic code. Smart contracts are immutable, and consequently, nobody can alter them after execution. The immutability binds all parties to an agreement as executed. This creates a consensus that does not rely on trust in any single party.
However, current smart contracts also contain several drawbacks. Exempli Gratia, due to smart contracts being based on information secured on a blockchain, and due to how miners around blockchain-based transaction data reach consensus. On these grounds, smart contracts cannot interact with external resources such as data feeds, API’s or traditional banking systems.
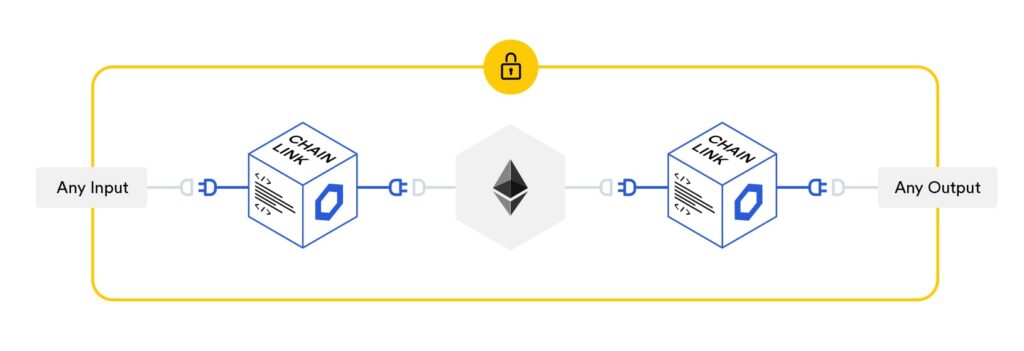
The way smart contract developers have traditionally solved this issue is through the use of a blockchain middleware called an “oracle.” Chainlink takes it one step further. They aim to solve the challenge with a secure oracle network. Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network is based on blockchain technology, allowing connectivity between smart contracts and external (or off-chain) resources.
Solution: Decentralized Oracles
Blockchains can’t directly access real-world data outside of their network by default. The relevance of oracles revolves around their ability to act as “agents.” Oracles need to find and verify real-world events and submit the information to smart contracts. Oracles transmit information from external data sources to smart contracts allowing contract execution along with predefined conditions.
Oracles are third-party services with a centralized point of control that are not part of the blockchain consensus mechanism. Therefore, one can question the trustworthiness of received data.
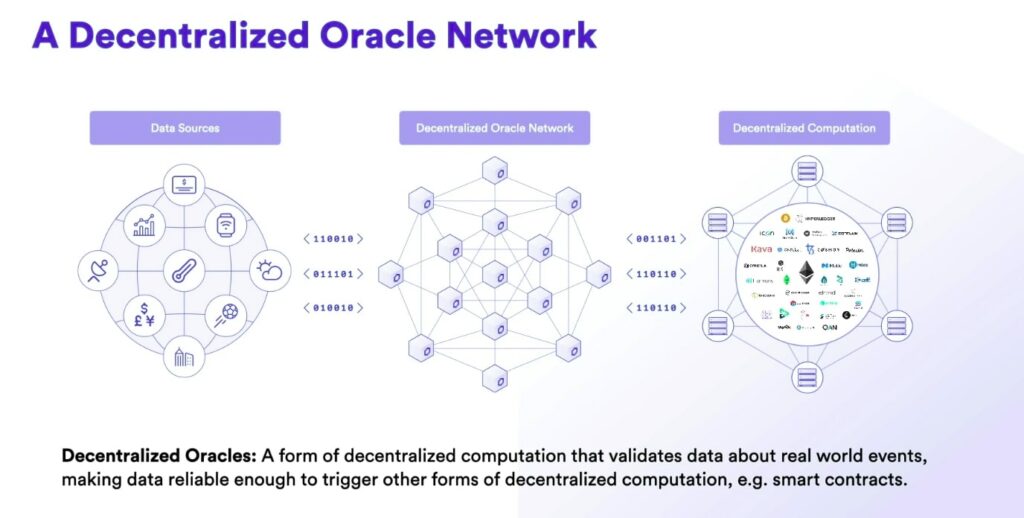
The Chainlink network developers intend to solve that issue by creating a decentralized oracle network for smart contracts. The network is to securely interact with resources external to the blockchain, such as cryptographically secure data feeds. Chainlink node operators are the backbone of the network. The nodes are what allows the network to fetch and transport the data from external sources. The network also facilitates interoperability between blockchains. Thanks to a secure off-chain computation process, the smart contracts become tamper-proof.
In summary, the company intends to solve one of the most prominent blockchain-related challenges by implementing decentralized oracles.
Chainlink is creating a billion-dollar bridge to the world of blockchain.
Sergey Nazarov, the creator of Chainlink Labs, revealed on the 5 of August 2021 the design for the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), a “new worldwide standard for decentralized inter-blockchain communications, data, and token transfers.” Along with the protocol, Chainlink announced the release of a Programmable Token Bridge that uses CCIP, as well as its automatic smart contracts (keepers).
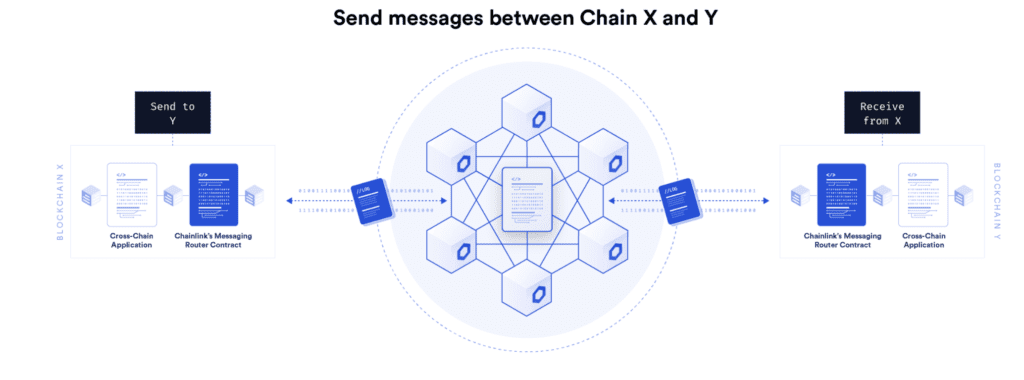
The initiatives involved will be disclosed during his SmartCon keynote. Although Chainlink’s CCIP will not be released for many months, the bridge project has already received “billions of dollars soft-committed from some of our biggest users,” according to Nazarov.
Chainlink offers a general association between many blockchain networks, taking advantage of the exceptional resources or benefits of each. Nazarov explains, “Just the same way that different applications on Ethereum use each other, now, different applications across different chains can use each other,”
Why Is Chainlink Important?
Chainlink offers a unique solution for transferring data in and out of blockchain, between the digital and “real” world. And their oracle service does this is in a decentralized and safe manner. Furthermore, Chainlink aims to solve the centralized oracle problem by a network of nodes, eliminating the single point of failure. Chainlink’s platform has attracted broad interest, also from institutions like Google and SWIFT. The project will continue to evolve as one of the most promising decentralized finance platforms for blockchain users and those interested in how to invest in DeFi.
LINK tokens are now available for buying, selling, and storing on Coinmotion.com.
