You must have heard before the phrases of “Proof of Work” (PoW) or “Proof of Stake” (PoS), and if so, probably you already know something about these concepts. They are called Blockchain consensus protocols.
In this post, I will explain these blockchain consensus protocols. Consensus protocols are the key operating feature of the distributed ledgers, but before I start describing protocols, we should understand Sybil Attacks and Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
Sybil attacks & Blockchain consensus protocols
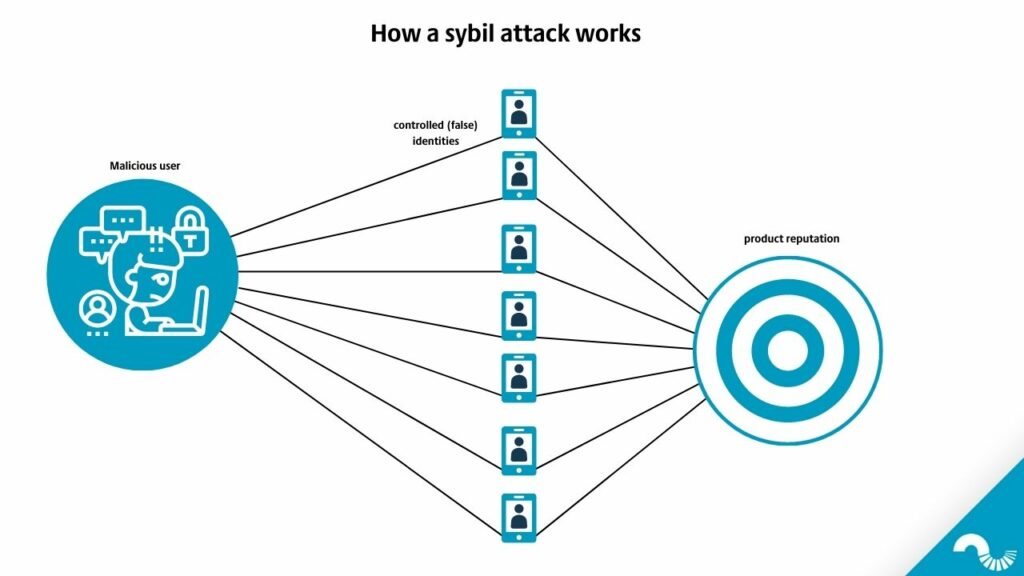
Let’s explain a Sybil attack in plain English — with an online marketplace analogy. Say, someone has two thousand different Amazon user profiles. This person writes lots of critical comments about the products. It isn’t easy to detect that these two thousand profiles are related. Sybil attack occurs when this individual consistently writes negative comments about a specific product, and the product’s rating goes down. The same thing could be pulled off by Twitter or Facebook bot accounts.
PoW, PoS, or other types of consensus protocols like proof of authority are designed to withstand these kinds of attacks.
Byzantine fault tolerance
Byzantine Fault Tolerance is another concept. Imagine four different Byzantine generals have armies, and they siege a city. Their armies are widely away from each other, so centralized authority is impossible.
They must decide the next move to attack or retreat. They only win if they do the same thing. When they decide how to proceed, all of them must make the same move. However, one of the generals might act differently — and the armies lose. Blockchain protocols prevent these kinds of acts as well.
In a blockchain, the Byzantine generals are nodes. Nodes do not truly trust each other, but they need a consensus for an actual ledger.
Nakamoto Consensus Protocol
Nakamoto Consensus Protocol (NCP) was the first blockchain consensus protocol. The name refers to Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin’s pseudonymous founder or founder.
NCP uses the Proof of Work protocol to make sure the authenticity of the block. Satoshi Nakamoto created bitcoin and blockchain technology. Using PoW and NCP makes it hard to hack or cheat the records.
Why do cryptocurrencies use these protocols? They use them because when you buy something, you do not want to pay twice. Every cryptocurrency uses one blockchain network, and every blockchain network uses consensus protocols to prevent double-spending.
Overview of The Most Popular Blockchain Consensus Protocols
Now we can look into some of the most popular blockchain consensus protocols. The most famous consensus protocols are PoW and PoS.
Proof of work
Proof of Work (PoW), the consensus protocol, works on a mathematical equation. For example, Bitcoin uses the SHA-256 cryptographic hash function. Miners try to solve that equation, and the one who finds it first gets the reward. When the work is done and proved, a new block adds to the blockchain.
Voices in cryptocurrency praise PoW for its security, namely its relative resistance to Sybil attacks and 51% attacks (the latter happens when one entity takes over 51% of the network and starts to control how new blocks add to the blockchain). PoW can’t prevent such attacks. What PoW does is makes the attacks too costly, as they require a huge amount of computing power.
PoW has some drawbacks too. The protocol needs more energy to work, and blocks take longer to add to the blockchain. Some inequality takes place as well: if someone has a lot of powerful machines for solving the PoW protocol’s mathematical question, they beat other miners. If speed and energy spending is a priority, then some cryptocurrencies choose different consensus protocols.
The proof of stake protocol
Proof of stake is another famous blockchain consensus protocol. PoS consensus protocol, like PoW, sets certain rules to govern the blockchain.
The PoS protocol selects miners randomly for solving the mathematical problem. For example, Ethereum tries to switch PoW to PoS, and it asks a minimum stake of 32 ether to be a miner. Maybe you have 1500 ether, but PoS protocol chooses another person who has 32 ether. Also, PoS consumes less energy than PoW which contributes to the popularity of proof of stake.
A notable disadvantage of PoS is lesser security than in PoW. In pursuit of scalability, proof of stake removes the “computationally unscalable” proof of work physical base, as the Etherplan blog puts it. This swap makes PoS systems subjective to attacks.
Delegated proof of stake protocol
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a different consensus protocol. It is a much more democratic system because every token owner can say something about the blockchain. Like in an everyday democracy in DPoS, the token holders use votes and select their representer. The representer’s role is to validate transactions and to make sure their node is working smoothly.
When the new block is added to the blockchain, the representer gets some tokens. Then the representer shares these tokens with its voters. However, if someone has more tokens, that person gets more shares.
DPoS uses less hardware and energy than PoS. One of the biggest disadvantages of the protocol is that sometimes delegates set up cartels and make the blockchain a less decentralized network.
Proof of space & proof of time: blockchain consensus protocols
Another important blockchain consensus protocol is Proof of Space and Time. Chia network uses PoST consensus protocol for its blockchain network. Proof of Space and Time protocol consists of two protocols, Proof of Space (PoS) and Proof of Time (PoT).
In PoST, the miner has some empty space in its system and voluntarily gives this space to the blockchain.
Provers demonstrate that they allot unused hard drive space for storage using the Proof of Space cryptography approach. Proof of Space must be linked to Proof of Time to be utilized as a consensus approach. PoT ensures that block times are consistent over time and so boosts the blockchain’s overall security.
Compared to PoW or PoS, Proof of Space and Time is a new consensus protocol. Like PoS, it consumes less energy and is faster than PoW protocol.
Proof of coverage
Lastly, I briefly explain the Proof of Coverage (POC) consensus protocol. PoC is used by Helium blockchain. In PoC protocol, radio waves are used by the algorithm to verify that Hotspots are providing valid wireless coverage. In other words, PoC tries to verify that Hotspots show their accurate locations and create wireless network coverage.
When the transactions are validated, and a new block is added to the blockchain, the miners get the rewards.
In this post, I shortly explain how the most used blockchain consensus protocols work and differ from each other. There are also other consensus protocols, and new coins will create their own consensus protocols in the future to solve particular issues.
What do you think about blockchain consensus protocols? Which one is the best for you and why?