The second-largest cryptocurrency Ethereum launched the London hard fork. If you are a crypto enthusiast, you must have heard about Ethereum 2.0 and the London hard fork. I will explain its importance to cryptocurrency investors in a simple way.
So what is Ethereum London hard fork?
London hard fork included five Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs), most notably EIP 1559 and EIP 3554, that aim to counter various inefficiencies.
EIP 1559 introduced a new fee structure to make Ethereum less inflationary. This protocol decreased miner revenue. And, EIP 3554 delayed Ethereum’s difficulty bomb to Dec. 1. This mechanism incrementally increases the difficulty of mining on the Ethereum network.

Gas fees after Ethereum London hard fork
The most significant change happened to transaction fees and included a new deflationary mechanism. Now, each block has a fixed, associated fee. This change came because of EIP 1559, included in the London update along with EIP 3238.
For example, if the Ethereum network fee is 30 Euro, sending 30 Euro worth of ETH is not worth it. These high fees made the network less attractive before the London hard fork, especially for new investors. EIP-1559 introduced a new transaction pricing mechanism that instead creates a base fee for each block’s transaction fee.
The base fee changes for each block depending on the demand. Moderating the volatility of base fees, this change will help bring more users into the crypto & ETH ecosystem.
ETH supply after Ethereum London hard fork
Meanwhile, the ETH blockchain burns the fee and thus reduces the overall supply of ETH. This effect creates deflationary pressure on ETH. In other words, the supply of ETH becomes limited — but in a different way than Bitcoin’s supply is. If a cryptocurrency supply is limited, the demand for it will grow over time, which may drive the price up.
Yep, unless someone objects in the next 24h, London should land on August 4th.
— Tim Beiko | timbeiko.eth (@TimBeiko) July 6, 2021
A few client teams have "👍'd" it already, but we want to be sure no one has a serious objection.
Keep an eye out 👀 https://t.co/KWRCvyrWR1
In short, Ethereum is a smart-contract platform and the first mover in this field. The majority of decentralized applications (DApps) and DeFi tokens (decentralized finance) are built upon its network. Decreased “gas” fees increase the demand for ETH and affect its price.

When is Ethereum London Fork?
The long-awaited London hard fork launched with block 12,965,000 on August 5, 2021 (European time, Aug 4 in the U.S.).
The Ethereum vocabulary
To understand the Ethereum London hard fork and the importance of this change, you should know some key definitions. They are blockchain, hard fork, Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and gas fees.
What is blockchain?
Cryptocurrencies are related to blockchain technology. Some people say that the biggest importance of Bitcoin is the creation of a blockchain. Blockchain is a database that stores every transaction. Ethereum blockchain consists of thousands of computers. Each computer or group of computers that hold its blockchain is in a different geographic location. They are all operated by separate individuals or groups of people. Those people are called the Ethereum community.
What is a hard fork in crypto?
If you want to make radical changes in the blockchain, you need a hard fork. A hard fork requires all nodes or users to upgrade to the latest version of the protocol software. If the community accepts the hard fork unanimously, the blockchain continues its way. However, sometimes not all developers accept the hard fork. In this situation, we get two blockchains, the old one and the new one. For example, this happened with Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, and Bitcoin Gold — but not with the ETH London fork.
Ethereum London hard fork, known as EIP 1559, radically changed the fee dynamics of Ethereum. It introduced a minimum fee to all on-chain transactions called the “base fee.”
What is a gas fee on Ethereum?
When someone wants to transfer ether to another address, gas, gas limit concepts, and gas prices come to action. Those are necessary to send an ETH transaction.
Theoretically, gas is a unit to measure the computational work of the transactions of smart contracts. Miners execute the trades at their own expense to keep the Ethereum network running. The gas prices or gas fees, or transaction fees mean the cost of Ether for every unit of gas needed to be paid.
If you want your transaction to go faster or your transfer is significant, you pay a bigger gas fee.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum London hard fork prepares the network’s evolution to what is called Ethereum 2.0. Eth 2.0 will mark the complete transition from the Pow consensus model to PoS.
ETH2 scaling for data will be available *before* ETH2 scaling for general computation. This implies that rollups will be the dominant scaling paradigm for at least a couple of years: first ~2-3k TPS with eth1 as data layer, then ~100k TPS with eth2 (phase 1). Adjust accordingly.
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) June 30, 2020
Currently, the Ethereum network can handle 15 to 45 transactions per second. According to Vitalik Buterin, one of the founders of Ethereum, when the blockchain finally transitions, 2.0 could eventually see the network speed up to around 100,000 transactions per second using sharing and other tactics.

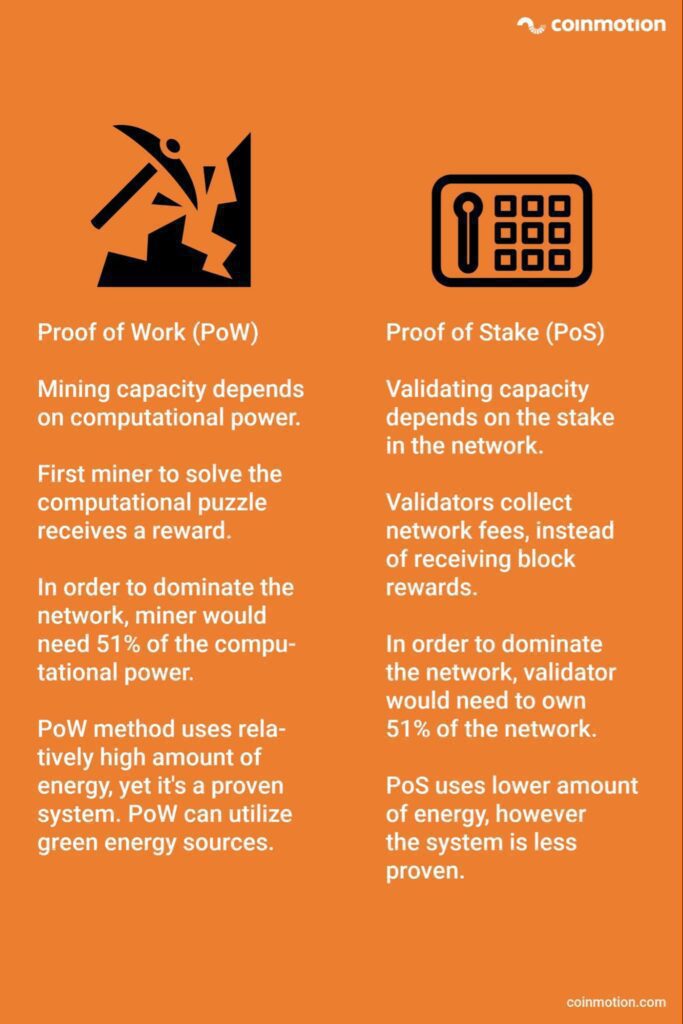
Proof of Work vs Proof of Stake
You must have heard about the Proof of Work. Proof of Work (PoW) is the mechanism that allows the decentralized cryptocurrency network to come to a consensus. I.e., agree on things like account balances and the order of transactions. This prevents Ethereum users from “double spending” their coins and ensures that the Ethereum chain is incredibly difficult to attack or overwrite.
What is Proof of Work (PoW)
I’ll explain the PoW logic by giving an example. Think about a big stadium. Maybe this stadium has 500,000 seats. Let’s suppose that one person hid a key behind one of the seats. In the PoW case, all miners try to find that key. Whoever finds that key gets the reward. This key allows the new block to be added to the blockchain.
However, PoW has some drawbacks. First, it consumes too much energy, which is terrible for the environment. Also, some mining pools could potentially dominate the mining game. This would lead to centralization and cause security risks.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)
Ethereum is in the process of switching from PoW to PoS. Ethereum Proof of Stake helps the decentralized network reach consensus securely. Proof-of-stake is the underlying mechanism that activates validators upon receiving enough stake from them. One key feature of the PoS is that it will not need to use a lot of energy.
For Ethereum, users need to stake 32 ETH to become a validator. Validators are chosen randomly to create blocks and are responsible for checking and confirming blocks they do not create. Validators earn rewards for proposing new blocks. If they attest to malicious blocks, they lose their stake.
Proof of Stake and Proof of Work: Explained By An Expert
Crypto enthusiasts argue which consensus mechanism is fairer. Is proof of stake better than proof of work? Some analysts argue that PoS is less secure than PoW. At the same time, PoS networks can scale times faster than PoW. Henry Brade, Executive Vice President at Coinmotion, Bitcoin & crypto enthusiast, explains the differences between the mechanisms:
“I think that the whole thing is a tradeoff. It seems that the more subjective (PoS) blockchains are much better and suit Decentral Finance purposes for technical scaling. Ethereum and Cardano are good examples of that. Of course, XRP is the network closest to fiat systems in terms of subjectivity.
However, for the purpose of truly decentralized, censorship-resistant, secure storing and transfer of value, and the role of digital gold, Bitcoin (based on PoW) is unbeatable. But it is a different use case.
In the long run, there will come a time when we will truly see the difference between PoS and PoW. It might take decades. But at some point, these PoS chains may be controlled over 50% by only a couple of wealthy entities. Those entities could be pressured to make changes to the rules of the system and the status of particular transactions. Meanwhile, Bitcoin will likely be immune to this. Then we will see the actual difference between these systems. But for now, it is hard to see.”
Ethereum London hard fork & ETH price predictions
The Ethereum forecast from Digitalcoin predicts that the ETH price will average around $2,707 in 2021 and rise to $3,382 in 2022. Over the longer term, it projects that the price will climb to an average of $5,852 in 2025 and $8,488 in 2028.
Just before the London hard fork, Ethereum, for the first time, flipped (dominated) Bitcoin by the number of daily active addresses on its network. Ethereum registered over 750,00 active addresses as of the 2nd of July, 2021. That is some 50,000 more than Bitcoin. Ethereum’s growing usage encourages very optimistic price forecasts.
Wall Street giant JPMorgan predicted Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake would also spur crypto adoption. Moreover — the transition will help generate $40 billion worth of value by 2025. After the change, Ethereum could become the most prominent cryptocurrency.

Ethereum upgrades: TL;DR
Ethereum is a smart contract platform that powers thousands of tokens and decentralized apps (dApps). Ethereum provides the infrastructure for all of them — but the network has become too clogged and cannot scale while transaction fees skyrocket. The Ethereum developers are upgrading the platform to make it scale, and the Ethereum London hard fork is part of this process.
What do you think about the Ethereum London hard fork? Do you believe the switch from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake will increase ETH prices? Tell us your thoughts in the comments.

ETH is in circulation because there are many miners receiving ETH and using it. If the process becomes unfeasible for miners, the coin price will drop and other GPU minable coins will appreciate. The example of what is already happening with ETC, ERG and RVN.
Good point, this factor also influences the ETH price predictions